HYDRAULIC RAILWAY SYSTEM
*All of the weight of the train is sustained by the hydraulic fluid eliminating the use of wheels.
*Does not consumes energy for flotation (it is a closed sealed hydraulic system).
*It works with extremely low hydraulic pressure, due the distribution of the fluid In a great contact surface. Approximately 142 psi (10kgf/cm2).
*The train slides with insignificant friction and abrasion.
*In parallel to the chinese Maglev that floats under magnetic repulsion, this system floats under hydraulic fluid, but does not consumes energy for its flotation and is extremely simple, allowing smaller production costs than the common railway system.
***New, non-obvious, useful (PCT/OMPI 2012).
HOW IT WORKS
1)The basis of sustaining are inside the trails.
2)The basis, in pairs, slides through the trails.
3)Each sustaining bases possess two fluid chambers, upper and lower.
4)The chambers are one over the other, in contrary position.
5)All of the train weight is over fluid reservoirs, that are located over the sustaining basis.
6)The reservoirs fluid pressure is transfered to the chambers by hydraulic hoses.
7)The lower chamber possess a larger opening contact area with the trail, than the upper chamber, making with all the set float and equalize inside the trails.
* The flow will be solved for a sealing system similar to the segmented rings system of the pistons of inner combustion engines, but without subdue to the high temperatures.
*Side tabs, similar to pulleys, maintain the train centered.
Observation: as the main idea is to propose the solution for the FRICTION, the biggest of the transport troubles, aren’t considered here systems of traction, suspension, brakes, etc.
ADVANTAGES
*Extreme simplicity.
*Low hydraulic pressure.
*Very low fuel consumption.
*The production cost is the same or ever cheaper than traditional system.
*Elimination of the friction and the abrasion caused by the mechanical parts attrition.
*It will possess great efficiency, durability and reduced maintenance costs.
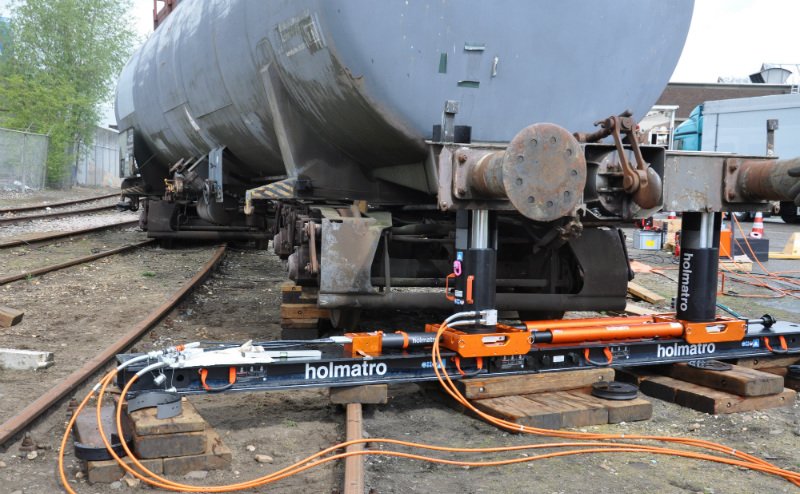


This work aims at value addition to the response in times of train derailments and accessibility to those areas which are inaccessible via rail during emergency situations, by combining the technological up-gradation and reduction in consumption of overhead time with the general principles of hydraulics; thus, contributing to the larger social cause of faster rescue and minimum train rescheduling in times of derailment in the Indian Railways. A rail-road vehicle is a vehicle which can operate both on rail tracks and a conventional road. Conventionally propulsion is through the tires, the rail wheels being free-rolling; the rail wheels are raised and lowered as needed but the authors’ design provides drive to the rail wheels for propulsion. The heavy load breakdown crane of the Indian Railways is its most important asset in Accident Response. But, the use of the existing breakdown cranes is limited only to tracks. Thus, bringing the crane to the site of the accident means travelling it over kilometres of railway lines which, in turn, means loss of response time. The design made by the authors includes the use of a hydraulic circuit for the lowering and lifting of rail and road wheels; the complete hydraulic system installed onto a convertible rail road truck provided with a breakdown crane that enables it to be operated either on road or on railway tracks, and to carry loaded or unloaded railway cars when on rail.
Learn moreThis article needs additional citations for verification.

The ČKD ČME3 is one of the longest-running and most-manufactured diesel–electric locomotives ever made.

These Pacific National-operated locos show three styles of diesel locomotive body: box cab (rear), hood unit (center) and cab unit (front).
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotive have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving wheels.